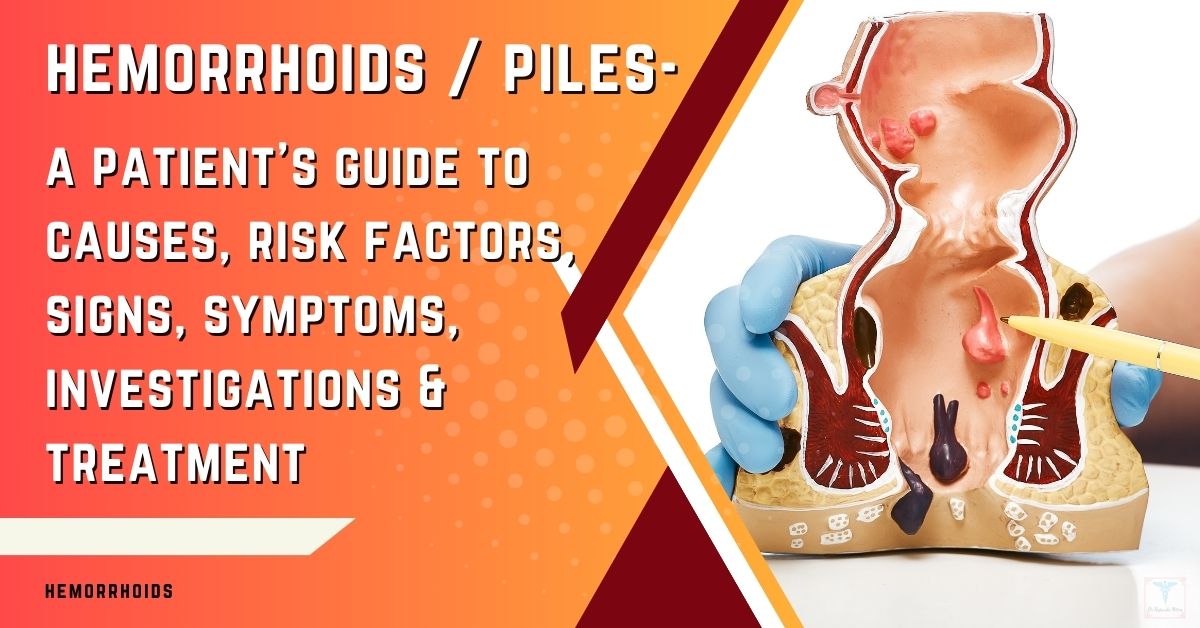
Diagnosing an anal fissure begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, bowel habits, risk factors, and duration of problems. How is anal fissure diagnosed – is an important factor before you actually opt for treatment.
Visually inspecting the anus and feeling for anal spasms provides important clues. Additional testing, like an anoscopy, may be done to confirm the diagnosis if needed. But in most straightforward cases, a doctor can definitively diagnose an anal fissure just based on a visual exam and your reported symptoms.
Let’s look at the typical diagnostic process in more detail.
Know How Is Anal Fissure Diagnosed – Key Points
- Detailed history and symptom review.
- Visual inspection and palpation of the anal area.
- Confirming visible lesion matches reported symptoms.
- Additional testing is needed only if the diagnosis is unclear.
Medical History and Symptoms
- Discuss your symptoms like pain, bleeding, and itching.
- Identify the duration and recurrent nature of symptoms.
- Review bowel habits, constipation, and straining.
- Note any relevant history like childbirth or Crohn’s.
Physical Exam and Visual Inspection
- Visual examination of the anal area.
- Looking for visible fissures, ulcers, and skin tags.
- Palpating for swollen, tender tissue.
- Checking for spasms of sphincter muscle.
- Confirming location matches fissure symptoms.
The visible anal lesion and correlating pain essentially confirm the diagnosis.
Additional Testing If Needed
- Anoscopy – inserting a tube to view the anal canal.
- Colonoscopy if atypical fissure or older age.
- Imaging like MRI for deep, atypical fissures.
- Lab tests if infection or other illness is suspected.
These are not necessary for most straightforward acute fissures but may be done if the diagnosis is uncertain or more details are needed.
Final Note From Dr. Rajarshi Mitra
Let me know if you need any clarification on how doctors diagnose anal fissures. The process is usually very straightforward based on a visual exam and your reported symptoms.