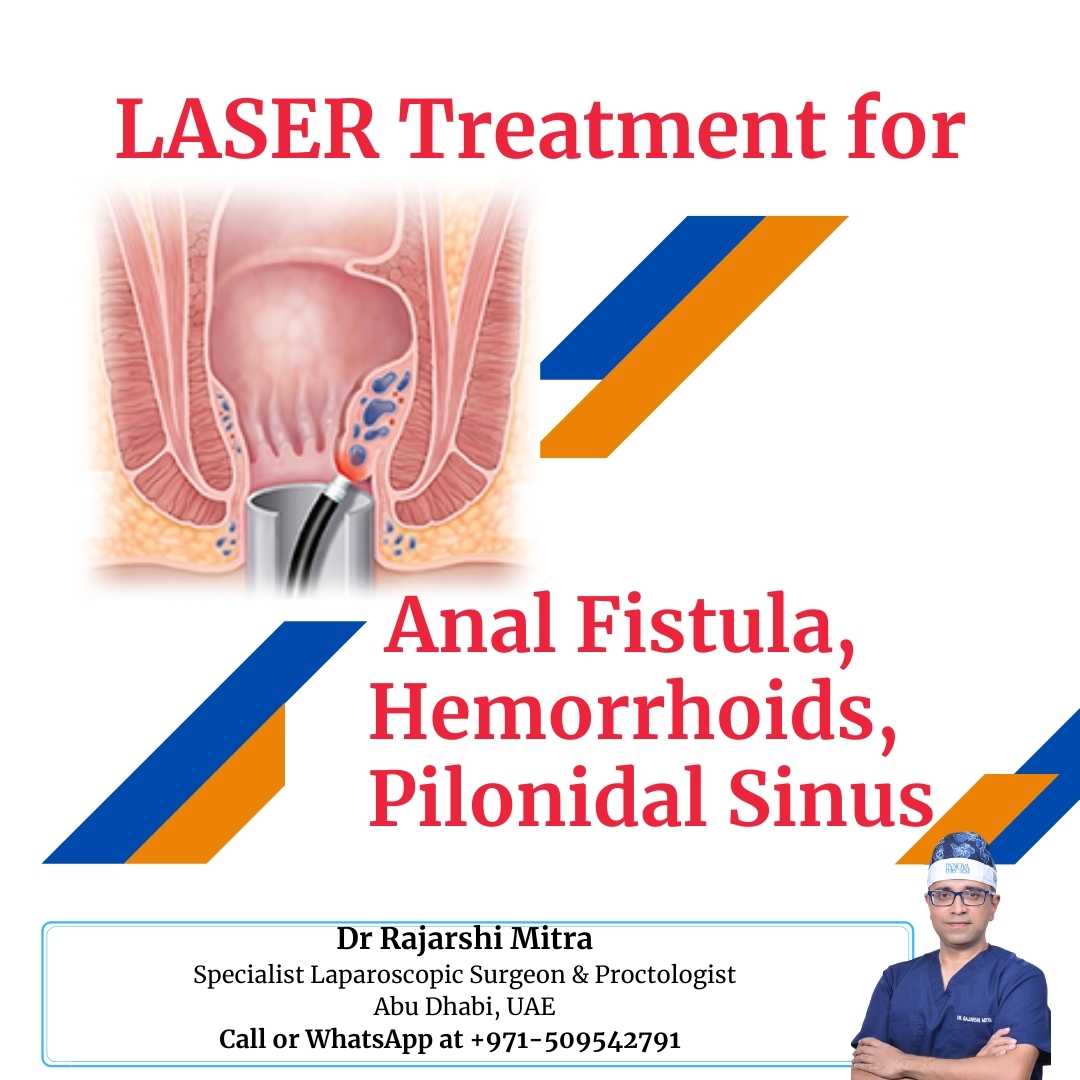
Consult with one of the best surgeons for
HEMORRHOIDS / PILES in Abu Dhabi
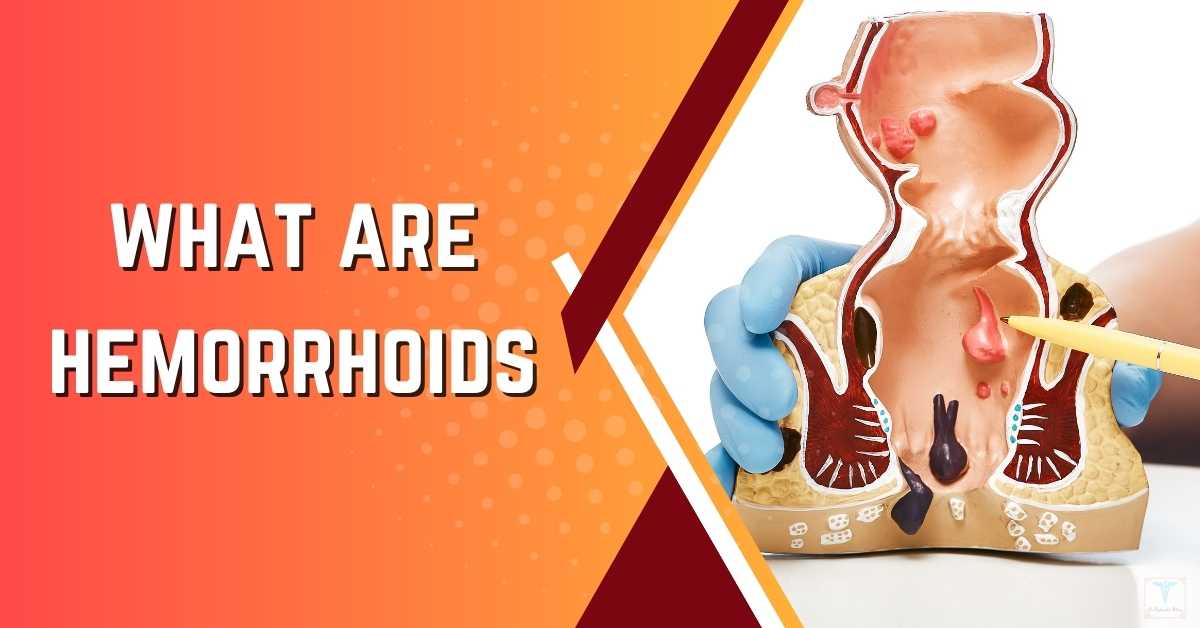
What are Hemorrhoids or Piles?
Hemorrhoids, also known as PILES, are cushions of blood vessels covered by a thin membrane of tissue, which are present within and around the lower part of our Anal Canal.
Why do we get Hemorrhoids?
The common causes of Hemorrhoids are:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for long periods of time on the toilet
- Having chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Being obese
- Being pregnant
- Faulty bowel function due to overuse of laxatives or enemas
- Eating a low-fiber diet
- Regular heavy lifting.
Why do Hemorrhoids or Piles form?
Most commonly, hemorrhoids are associated with long standing constipation, prolonged straining during bowel movements, and prolonged sitting on the toilet – all of which result in swelling and bulging of the blood vessels. This is also why hemorrhoids are usually common during pregnancy, when the enlarging uterus presses on the veins and result in the swelling of the blood vessels.
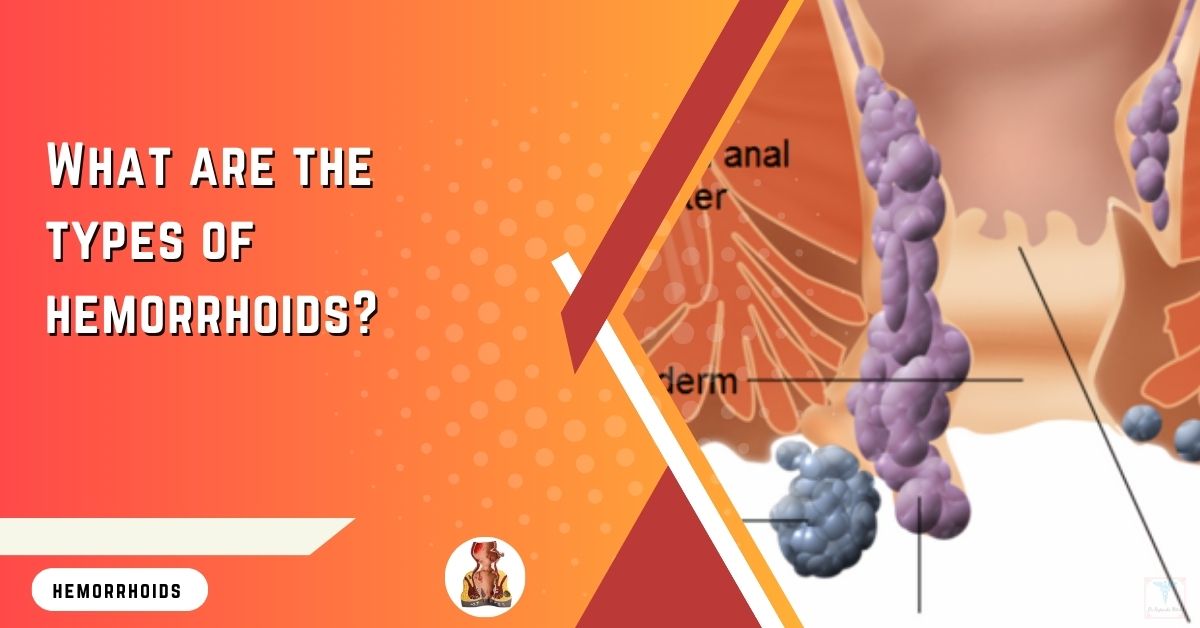
What are the types of Hemorrhoids?
There are usually Two types of Hemorrhoids.
Internal Hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids.
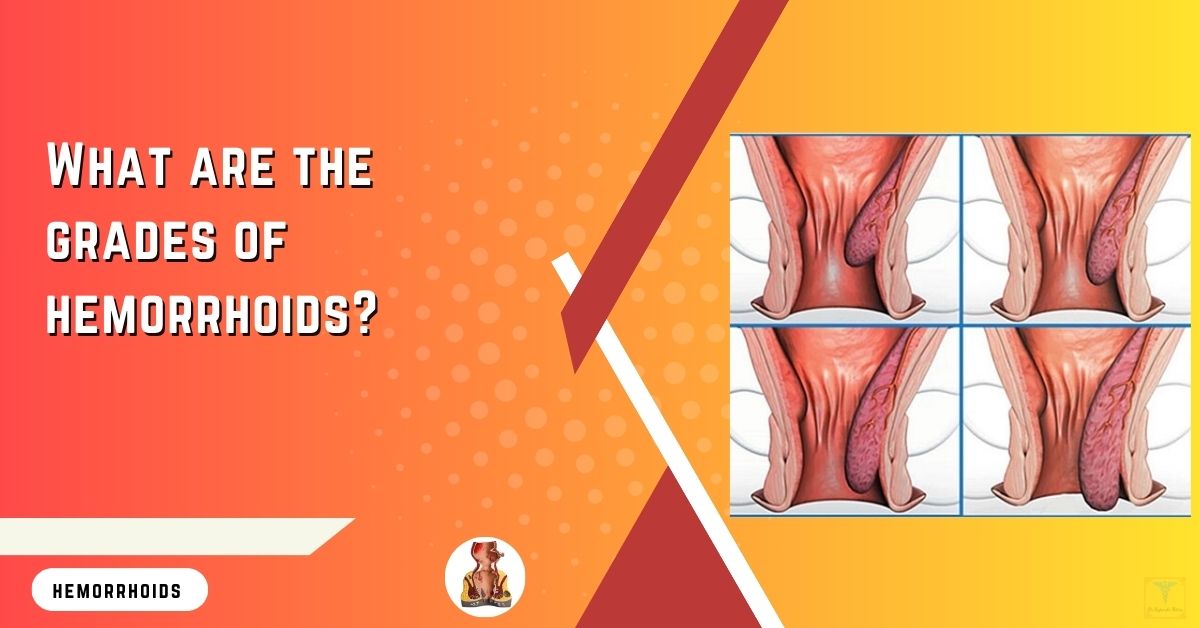
What are the Grades of Hemorrhoids?
Usually Internal Hemorrhoids are classified in 4 Grades:
- Grade I hemorrhoids project into the anal canal and often bleed but do not prolapse
- Grade II hemorrhoids may protrude beyond the anal verge with straining or defecating but reduce spontaneously when straining ceases (i.e. return to their resting point by themselves)
- Grade III hemorrhoids protrude spontaneously or with straining and require manual reduction (i.e. require manual effort for replacement into the anal canal)
- Grade IV hemorrhoids chronically prolapse and cannot be reduced; these lesions usually contain both internal and external components and may present with acute thrombosis or strangulation
What are the common symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
The common symptoms of Hemorrhoids are:
- Bleeding during bowel movements
- Protrusion of skin during bowel movements
- Feeling of a lump coming out of anal canal while passing stool
- Itching in the anal area
- Pain in the anal area
- Sensitive lump(s)
What are the Complications of Hemorrhoids?
Complications of Hemorrhoids can be:
- Rarely, chronic blood loss from hemorrhoids may cause anemia, in which you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to your cells.
- Strangulated hemorrhoid: If the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, the hemorrhoid may be “strangulated,” which can cause extreme pain.
- Blood clot: Occasionally, a clot can form in a hemorrhoid (thrombosed hemorrhoid). Although not dangerous, it can be extremely painful and sometimes needs to be lanced and drained.
How can I prevent Hemorrhoids?
The best way to prevent hemorrhoids is to keep your stools soft, so they pass easily. To prevent hemorrhoids and reduce symptoms of hemorrhoids, follow these tips:
Eat high-fiber foods
Drink plenty of fluids
Consider fiber supplements
Don’t strain
Go as soon as you feel the urge
Avoid long periods of sitting
Stay Active
What are the Medical Treatment for Hemorrhoids?
- Eating a high-fiber diet and taking over-the-counter fiber supplements (25-35 grams of fiber/day) to make stools soft, formed and bulky.
- Avoiding excessive straining to reduce the pressure on hemorrhoids and help prevent protrusion.
- Drinking more water to help prevent hard stools and aid in healing.
- Taking warm tub baths (sitz baths) for 10 to 20 minutes, a few times per day to help the healing process.
What are the Surgical Treatment for Hemorrhoids?
MINIMAL INVASIVE SURGERY FOR HEMORRHOIDS:
Majority of the Hemorrhoids today, can be managed by Minimal Invasive surgery, without the need for a painful open surgery.
The healing process is very fast and most can be managed as a Day Care Surgery.
The options for Minimal Invasive Surgery for Hemorrhoids include:
LASER HEMORRHOIDOPLASTY
DOPPLER GUIDED THD WITH MUCOPEXY
STAPPLER HEMORRHOIDOPEXY
HAL-RAR.
Other Options for the Surgical Treatment of Hemorrhoids include:
Closed Hemorrhoidectomy
Injection Sclerotherapy
Rubber Band Ligation( Legacy procedure and not a complete treatment)
HEMORRHOIDS
WHAT ARE HEMORRHOIDS?
Hemorrhoids, also known as PILES, are cushions of blood vessels covered by a thin membrane of tissue, which are present within and around the lower part of our Anal Canal.
WHY DO WE GET HEMORRHOIDS?
Common Causes of Hemorrhoids
The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Hemorrhoids can develop from increased pressure in the lower rectum due to:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for long periods of time on the toilet
- Having chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Being obese
- Being pregnant
- Faulty bowel function due to overuse of laxatives or enemas
- Eating a low-fiber diet
- Regular heavy lifting.
WHY DO HEMORRHOIDS FORM?
The tissues supporting the cushions of blood vessel can usually stretch due to any cause of increased pressure, esp. when straining to pass stools or when a patient is constipated. As a result, the vessels expand, the walls thin out and bleeding occurs. When the stretching and pressure continue, the weakened vessels can start protruding.
Most commonly, hemorrhoids are associated with long standing constipation, prolonged straining during bowel movements, and prolonged sitting on the toilet – all of which result in swelling and bulging of the blood vessels. This is also why hemorrhoids are usually common during pregnancy, when the enlarging uterus presses on the veins and result in the swelling of the blood vessels.
TYPES OF HEMORRHOIDS
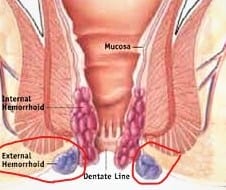
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF HEMORRHOIDS?
There are usually Two types of Hemorrhoids.
Internal Hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids.
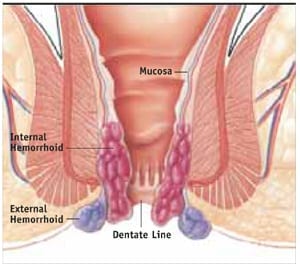
EXTERNAL HEMORRHOIDS
External Hemorrhoids develop in the skin around the external anal opening.
Symptoms:
Swelling or feeling a lump around the anus
Discomfort
Pain if the blood vessels get thrombosed (clotted blood)
Bleeding if the skin over the Hemorrhoids tears.
INTERNAL HEMORRHOIDS
Internal hemorrhoids lie inside the rectum. You usually can’t see or feel them, and they rarely cause discomfort. But straining or irritation when passing stool can cause:
- Painless bleeding during bowel movements. You might notice small amounts of bright red blood on your toilet tissue or in the toilet.
- A hemorrhoid to push through the anal opening (prolapsed or protruding hemorrhoid), resulting in pain and irritation.
GRADES OF HEMORRHOIDS
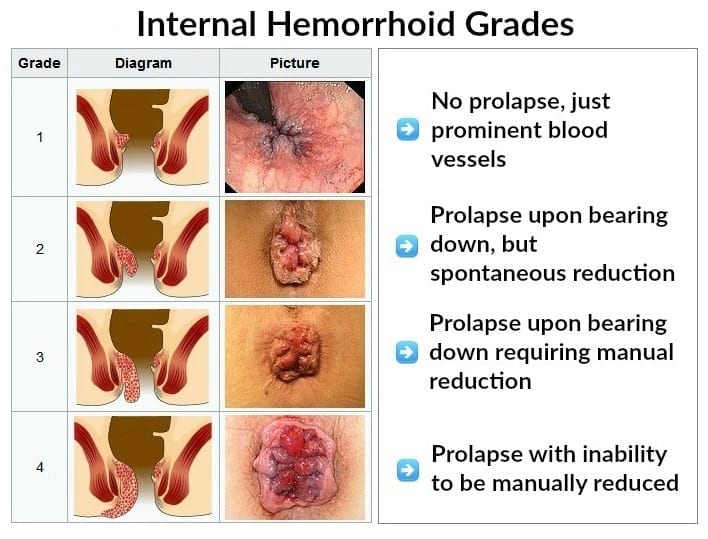
WHAT ARE THE GRADES OF HEMORRHOIDS??
Usually Internal Hemorrhoids are classified in 4 Grades:
- Grade I hemorrhoids project into the anal canal and often bleed but do not prolapse
- Grade II hemorrhoids may protrude beyond the anal verge with straining or defecating but reduce spontaneously when straining ceases (i.e. return to their resting point by themselves)
- Grade III hemorrhoids protrude spontaneously or with straining and require manual reduction (i.e. require manual effort for replacement into the anal canal)
- Grade IV hemorrhoids chronically prolapse and cannot be reduced; these lesions usually contain both internal and external components and may present with acute thrombosis or strangulation
SYMPTOMS OF HEMORRHOIDS

WHAT ARE THE COMMON SYMPTOMS OF HEMORRHOIDS?
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Any of the following may be a sign of hemorrhoids:
- Bleeding during bowel movements
- Protrusion of skin during bowel movements
- Feeling of a lump coming out of anal canal while passing stool
- Itching in the anal area
- Pain in the anal area
- Sensitive lump(s)
COMPLICATIONS OF HEMORRHOIDS
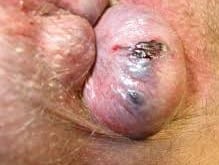
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF HEMORRHOIDS?
Complications of hemorrhoids are rare but include:
- Rarely, chronic blood loss from hemorrhoids may cause anemia, in which you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to your cells.
- Strangulated hemorrhoid: If the blood supply to an internal hemorrhoid is cut off, the hemorrhoid may be “strangulated,” which can cause extreme pain.
- Blood clot: Occasionally, a clot can form in a hemorrhoid (thrombosed hemorrhoid). Although not dangerous, it can be extremely painful and sometimes needs to be lanced and drained.
PREVENTION OF HEMORRHOIDS

HOW CAN I PREVENT HEMORRHOIDS FROM FORMING?
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
The best way to prevent hemorrhoids is to keep your stools soft, so they pass easily. To prevent hemorrhoids and reduce symptoms of hemorrhoids, follow these tips:
- Eat high-fiber foods: Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Doing so softens the stool and increases its bulk, which will help you avoid the straining that can cause hemorrhoids. Add fiber to your diet slowly to avoid problems with gas.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Drink six to eight glasses of water and other liquids (not alcohol) each day to help keep stools soft.
- Consider fiber supplements: Most people don’t get enough of the recommended amount of fiber – 20 to 30 grams a day – in their diet. Studies have shown that over-the-counter fiber supplements, such as psyllium, improve overall symptoms and bleeding from hemorrhoids.
If you use fiber supplements, be sure to drink at least eight glasses of water or other fluids every day. Otherwise, the supplements can cause or worsen constipation.
- Don’t strain: Straining and holding your breath when trying to pass a stool creates greater pressure in the veins in the lower rectum.
- Go as soon as you feel the urge: If you wait to pass a bowel movement and the urge goes away, your stool could dry out and be harder to pass.
- Stay active to help prevent constipation and to reduce pressure on veins, which can occur with long periods of standing or sitting. Exercise can also help you lose excess weight that might be contributing to your hemorrhoids.
- Avoid long periods of sitting: Sitting too long, particularly on the toilet, can increase the pressure on the veins in the anus.
TREATMENT FOR HEMORRHOIDS


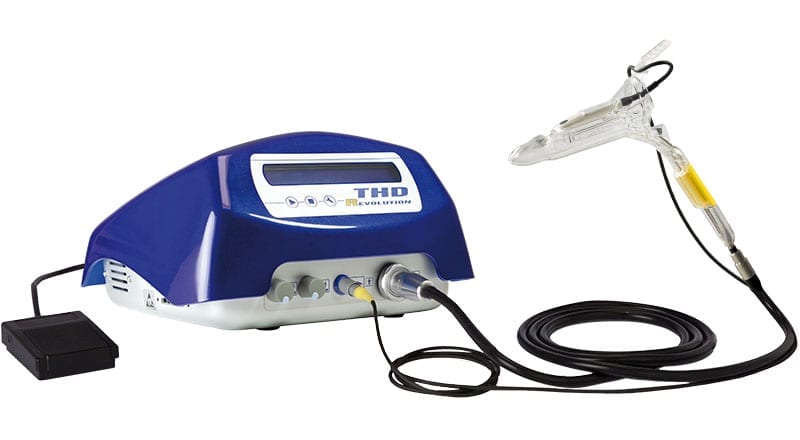
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR HEMORRHOIDS?
Treatment for Hemorrhoids can be either:
Non-Surgical or Medical Management
Surgical Treatment.
NONSURGICAL TREATMENT
It is important that symptoms are checked by a surgeon experienced in managing and treating hemorrhoids first before you try self-treatments. They will perform a thorough examination and recommend treatment. Mild symptoms can be relieved frequently without surgery. With nonsurgical treatment, pain and swelling usually decrease in two to seven days. The firm lump should recede within four to six weeks.
Treatment includes:
- Eating a high-fiber diet and taking over-the-counter fiber supplements (25-35 grams of fiber/day) to make stools soft, formed and bulky.
- Avoiding excessive straining to reduce the pressure on hemorrhoids and help prevent protrusion.
- Drinking more water to help prevent hard stools and aid in healing.
- Taking warm tub baths (sitz baths) for 10 to 20 minutes, a few times per day to help the healing process.
SURGICAL TREATMENT FOR HEMORRHOIDS:
A wide variety of different surgical approaches are available for the treatment of symptomatic Hemorrhoids.
After examining the hemorrhoids, your surgeon will decide on the proper surgical treatment for your hemorrhoids and discuss the benefits of that particular procedure.
MINIMAL INVASIVE SURGERY FOR HEMORRHOIDS:
Majority of the Hemorrhoids today, can be managed by Minimal Invasive surgery, without the need for a painful open surgery.
The healing process is very fast and most can be managed as a Day Care Surgery.
The options for Minimal Invasive Surgery for Hemorrhoids include:
- LASER HEMORRHOIDOPLASTY
- DOPPLER GUIDED THD WITH MUCOPEXY
- STAPPLER HEMORRHOIDOPEXY
- HAL-RAR.
Other Options for the Surgical Treatment of Hemorrhoids include:
Closed Hemorrhoidectomy
Injection Sclerotherapy
Rubber Band Ligation( Legacy procedure and not a complete treatment)